Gastrointestinal Preclinical
Disease Models
- 10 septembre, 2021
- 06 juillet, 2021
The next Emesis/Nausea Session in ferret
- 17 avril, 2019
Microbiome & Probiotics Series
With our extensive experience in developing gastrointestinal disease models, such as IBD preclinical, Emesis & Nausea, IBS, Gastric motility, our Gastroenterology (GI) department made Syncrosome one of the leaders in GI pathologies in the Contract Research Organization’s world. Indeed, our first disease models as a non-clinical CRO were developed in this therapeutic area.
Gastrointestinal disease models
In addition to our knowledge of animal models and in histological biomarkers, we were able to provide new answers to our customers needs with the use of cellular inflammation biomarkers, which provides complementary responses in models like IBD preclinical (MPO activity, ELISA, Cytokines, etc…) and the development of new techniques. Our disease models (guinea pigs, piglets, ferrets, rats or mice depending on the pathology) are fitted for testing disease-modifying drug or compounds acting on symptomatic effects. Depending on your needs, it is possible to perform classical, Per Os, Intravenous (IV), Intraperitoneal (IP) or Intrarectal administration.
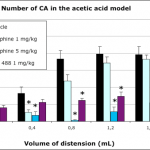
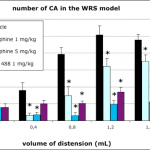
- Colorectal distension with chemical or mechanical sensitization
- Chemical induction: acetic acid or others
- Visceral Pain
- Manometric recording
- Number and intensity of abdominal contractions can be evaluated
- This syndrome could be associated with other pathologies and be used to test nutraceuticals or functional food
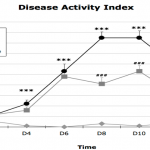
- Chemical induction with DSS administration
- Several degrees of inflammation
- Ulcerative colitis (Small Intestine), Crohn’s Disease (Colon)
- Disease Activity Index (DAI): reproducible and measurable parameters (Body weight, blood culture, faeces analysis)
- Inflammation, Myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, ELISA dosage (cytokines level), Histology
- Inflammatory parameters followed thanks to histology and ELISA tests (MPO, Cytokines…)
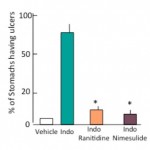
- Pharmacological induction: Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- Chemical Induction by using Indomethacin
- Gastric lesions quantification
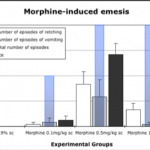
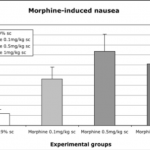
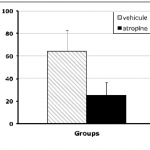
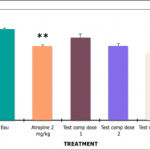
- Detection of potential antiemetic effects of compounds
- Retching, vomiting, nausea-like behavior
- Nausea and emesis events individually analyzed
- Evaluation of a compound’s effect on gut motility
- Distance covered by charcoal and transit percentage
- Percentage of remaining red phenol in the stomach